Sustainable student living emphasizes eco-friendly building materials like bamboo and recycled steel, energy-efficient windows, natural insulation, and locally sourced materials to minimize environmental impacts. Efficient water management through conservation strategies and rainwater harvesting, waste reduction via recycling, composting, and reusable items, and renewable energy sources like solar panels further enhance sustainability. Campus communities also prioritize green transportation options, encouraging students to adopt eco-conscious practices that extend beyond their academic years.
In today’s digital era, sustainable student living is not just a trend but a necessity. Eco-friendly student housing practices play a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact of campuses while fostering a healthier planet. This article explores various strategies, from green building materials and energy efficiency to sustainable water management and renewable energy sources. By implementing these practices, student halls can become models for eco-conscious living, encouraging a future where every individual contributes to a greener world.
- Green Building Materials: Choosing Eco-Conscious Options
- Energy Efficiency: Reducing Student Housing Carbon Footprint
- Sustainable Water Management: Conserving Resources in Dorms
- Waste Reduction Strategies for Efficient Living Spaces
- Renewable Energy Sources: Powering Student Halls Sustainably
- Eco-Friendly Transportation: Encouraging Green Commutes on Campus
Green Building Materials: Choosing Eco-Conscious Options

Student housing is undergoing a green revolution, with an increasing focus on sustainable student living. One key aspect is the selection of eco-friendly building materials. This shift involves choosing options that are not only environmentally responsible but also cost-effective and durable. Materials like bamboo, recycled steel, and energy-efficient windows are gaining popularity in new constructions and renovations. These choices reduce carbon footprints by minimizing deforestation (bamboo) and manufacturing impacts (recycled steel), while energy-efficient windows lower heating and cooling costs.
Furthermore, incorporating natural insulation materials such as sheep’s wool or cellulose made from recycled paper can significantly enhance a building’s energy efficiency. Additionally, utilizing locally sourced materials reduces the carbon emissions associated with transportation. This holistic approach to green building ensures that student housing not only supports environmental sustainability but also offers healthier and more comfortable living spaces for residents.
Energy Efficiency: Reducing Student Housing Carbon Footprint

Student housing plays a significant role in shaping the environmental footprint of young lives. One of the most impactful ways to foster sustainable student living is by prioritizing energy efficiency. This involves adopting practices that reduce power consumption and, consequently, lower carbon emissions. Simple measures such as LED lighting, smart thermostats, and energy-efficient appliances can significantly cut down electricity usage in dormitories and shared spaces.
Furthermore, encouraging residents to turn off lights and electronics when not in use, along with proper insulation and efficient window treatments, can create a more energy-conscious environment. By integrating these practices, student housing providers can reduce their carbon footprint while also teaching young individuals the value of eco-friendly living, fostering a generation committed to sustainable practices beyond their academic years.
Sustainable Water Management: Conserving Resources in Dorms

In sustainable student living, efficient water management is a key practice. Dormitories can significantly reduce their water footprint by implementing simple yet effective conservation strategies. This includes installing low-flow fixtures in bathrooms and kitchens, such as showerheads and faucets, which decrease water usage without compromising performance. Additionally, adding dual-flush toilets can dramatically cut down on water waste by providing an option for liquid waste during normal usage and solid waste when needed.
Beyond hardware, behavioral changes play a crucial role. Encouraging residents to adopt habits like turning off taps while brushing teeth or washing hands, as well as using laundry machines only when full, further conserves this precious resource. Some institutions also employ rainwater harvesting systems for non-potable uses, such as irrigation or flushing toilets, reducing the strain on municipal water supplies and fostering a more eco-friendly learning environment.
Waste Reduction Strategies for Efficient Living Spaces
In the pursuit of sustainable student living, waste reduction strategies are paramount in efficient living spaces. Students can significantly contribute to eco-friendliness by adopting simple practices such as recycling and composting, which help divert waste from landfills. Encouraging the use of reusable items like water bottles, coffee cups, and shopping bags can further minimize single-use plastic consumption. Efficient lighting systems, including LED bulbs, not only save energy but also reduce electricity bills.
Smart management of resources is another key aspect. Implementing water conservation measures such as fixing leaks, installing low-flow fixtures, and promoting responsible washing practices can significantly cut down on water usage. Similarly, proper insulation and energy-efficient appliances play a crucial role in reducing energy consumption, leading to more environmentally conscious and cost-effective living environments for students.
Renewable Energy Sources: Powering Student Halls Sustainably

Student housing is a key area for implementing renewable energy sources, aiming to achieve sustainable student living. By embracing alternatives to traditional fossil fuels, student halls can significantly reduce their carbon footprint. Solar panels are an increasingly popular choice, leveraging the sun’s power to generate electricity. Wind turbines, though less common on campuses, offer another way to harness clean energy from nature’s resources.
Integrating these renewable energy sources not only contributes to a greener environment but also fosters awareness among students about sustainable practices. Many universities are leading the way by investing in such initiatives, setting an example for eco-friendly student living and encouraging broader adoption of sustainable strategies both on campus and beyond.
Eco-Friendly Transportation: Encouraging Green Commutes on Campus
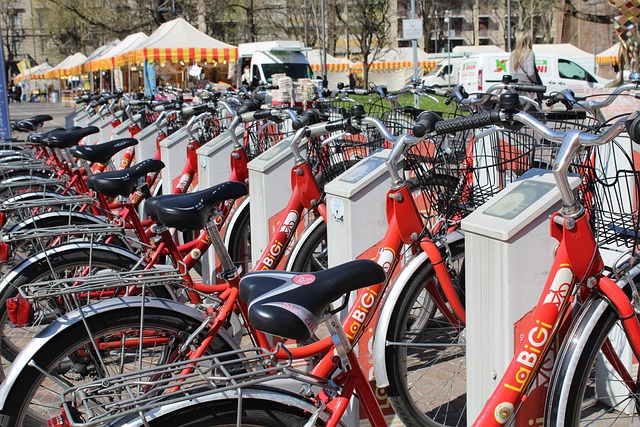

In the realm of sustainable student living, campus communities are increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly transportation options to encourage green commutes. This shift is driven by a collective goal to reduce carbon footprints and promote healthier, more environmentally conscious lifestyles among students. By implementing initiatives like dedicated bike lanes, electric vehicle charging stations, and discounted public transit passes, universities can significantly cut down on vehicular emissions and foster a culture of responsible sustainability.
Beyond these measures, campuses are leveraging technology to optimize transportation networks, reducing the need for individual car trips. Shared ride programs, dynamic shuttle services, and app-based ridesharing platforms not only alleviate traffic congestion but also offer students convenient and eco-conscious ways to traverse campus. These practices demonstrate a holistic approach to sustainable student living, where every journey contributes to a greener future.